Two key modules of the AdMiRe system architectures are Background Extraction and Super Resolution applications.
Super resolution application has the task of increasing the resolution of portions of a video to match it to the definition of the professionally captured content in the studio which is in HD or 4K. Most smart phones and webcams cannot deliver such high-resolution contents, especially if only portions of the captured frame are of interest. There is a very sizable state of the art in super resolution in the literature. However, most such approaches, although offering very good performance in terms of the quality of results, cannot be performed in real-time because they have been primarily designed for image processing or processing of already captured video, for which the processing time is not as critical as in AdMiRe use cases, where super resolution should perform in real-time. For 16 months the AdMiRe project analyzed the state-of-the-art techniques in super resolution, selected the most promising, and designed an original approach for super resolution in compressed domain. The most promising candidates after assessment of their performance in terms of quality of the results and computational complexity, as well as other criteria such as latency and impact of compression artifact were implemented. The retained solution for integration in the AdMiRe project is based on NVIDIA Maxine, an SDK released in August 2021 which is optimized in terms of computational complexity and was the only solution that could reach real-time requirements in AdMiRe use case. Another approach based on a solution designed by EPFL that performs super resolution in the compressed domain was contributed to JPEG standardization committee and is now used as an anchor in the upcoming call for proposals of JPEG standardization effort. The latter technique is planned to be open sourced at the conclusion of the project. Details about the super resolution application can be found in the deliverable D3.2 of AdMiRe which is publicly accessible from its website.
Background Extraction application has the task of removing in real time the background of the remote participants when they do not have access to green screens. For 16 months the AdMiRe project analyzed the state-of-the-art techniques in background segmentation, selected the most promising, designed an original approach and implementation the most promising candidates after assessment of their performance in terms of quality of the results and computational complexity, as well as other criteria such as latency and impact of compression artifact. Two final applications were finally retained and selected for integration to the rest of the project. One approach is based on NVIDIA Maxine, an SDK released in August 2021 which is optimized in terms of computational and offers good results for typical head and shoulder content. Another approach is based on a solution designed by EPFL in the framework of the project which offers superior performance in terms of quality and can cope with more challenging contents. The latter has been also optimized in terms of computational complexity and has been demonstrated to show real-time performance in use cases identified by the project. The latter technique is planned to be open sourced at the conclusion of the project after further analysis in an end-to-end system in trials carried out in the project planned in 2022. Details about the background extraction application can be found in the deliverable D3.3 of AdMiRe which is publicly accessible from its website.
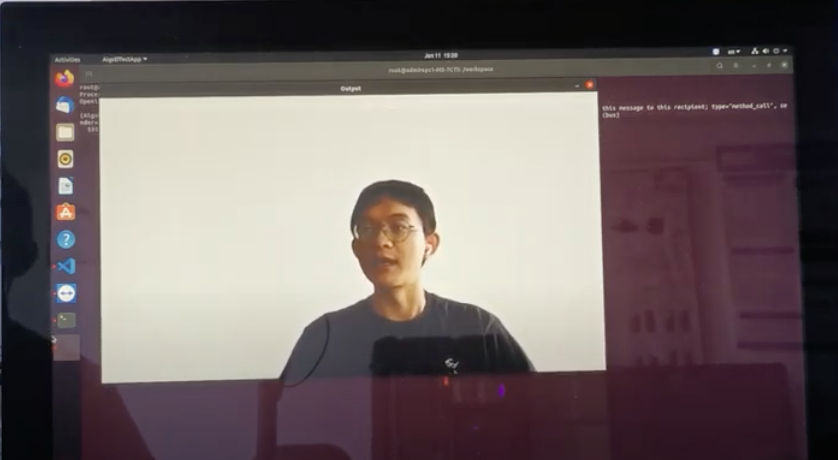
Video demonstrating the real-time performance of background extraction: